Guia definitivo para Segurança de Dados
A segurança de dados capacita sua equipe a trabalhar com segurança em todos os lugares, enquanto acessa os dados de negócios de qualquer lugar. Saiba como a Forcepoint torna isso possível.
Os dados são ouro digital para pessoas, empresas e governos. E à medida que o local de trabalho moderno se transforma rapidamente em forças de trabalho híbridas e serviços baseados na nuvem, um cenário de ameaças em constante evolução significa que as organizações devem fornecer aos dados o tempo, a atenção e a tecnologia necessários para mantê-los seguros.
Isso significa que a proteção das informações confidenciais e proprietárias contra vazamentos e violações de dados é uma parte tão importante do sucesso quanto a proteção dos lucros.
Neste guia
Obtenha explicações sobre os principais conceitos relacionados à segurança de dados, juntamente com links para recursos e ferramentas adicionais que ajudarão você a entender e implementar com sucesso as melhores práticas de segurança de dados.
Fundamentos da Segurança de Dados
O que é Segurança de Dados?
A segurança de dados refere-se a todas as práticas e medidas adotadas para proteger os dados contra acesso, uso, divulgação, interrupção, modificação ou destruição não autorizados. Abrange uma ampla gama de técnicas, tecnologias, políticas e procedimentos projetados em torno do conceito de prevenção contra perda de dados para garantir sua confidencialidade, integridade e disponibilidade.
Uma violação de segurança de dados pode acarretar consequências graves, incluindo perdas financeiras, danos à reputação, responsabilidade legal e perda de confiança do público. Organizações e pessoas físicas têm um interesse próprio em manter a segurança de seus dados para evitar que agentes de ameaças tenham acesso aos mesmos.
O progresso da tecnologia e a crescente interconexão de dados fazem com que novos desafios e riscos surjam com o tempo. O surgimento da computação em nuvem, dos dispositivos portáteis e da Internet das Coisas (IoT, Internet of Things) ampliou a superfície de ataque para muitas organizações e aumentou a complexidade da segurança de dados. Agora, uma revolução de Inteligência Artificial (IA) generativa está reinventando o risco de dados, mais uma vez.
Devido a essa tendência contínua, é indispensável uma abordagem holística para a segurança de dados, que considere todo o ciclo de vida dos dados. Na Forcepoint, isso inclui dar muita atenção à descoberta, classificação, priorização, proteção e monitoramento de dados em toda a empresa.
Quando implementada corretamente, a segurança de dados envolve várias camadas de proteção, como:
Segurança física
- Controles de acesso baseados em função
- Vigilância por vídeo
- Instalações de armazenamento seguras
- Pessoal de segurança
Salvaguardas técnicas
- Software de prevenção contra a perda de dados
- Criptografia
- Mecanismos de autenticação multifatores
- Firewalls
- Sistemas de prevenção de invasões
- Software antivírus
Políticas e procedimentos
- Níveis de classificação de dados
- Práticas de retenção e destruição de dados
- Treinamento de funcionários em melhores práticas de segurança de dados
Tipos de Segurança de Dados
O risco de dados decorre dos aplicativos pelos quais os dados passam e nos quais são usados. Por isso, existem vários subtipos de segurança de dados sobre os quais as organizações devem estar cientes.
Quer você empregue uma abordagem fragmentada ou abrangente para aplicar soluções de segurança, é importante considerar esses conceitos importantes dentro da sua estratégia de segurança de dados.
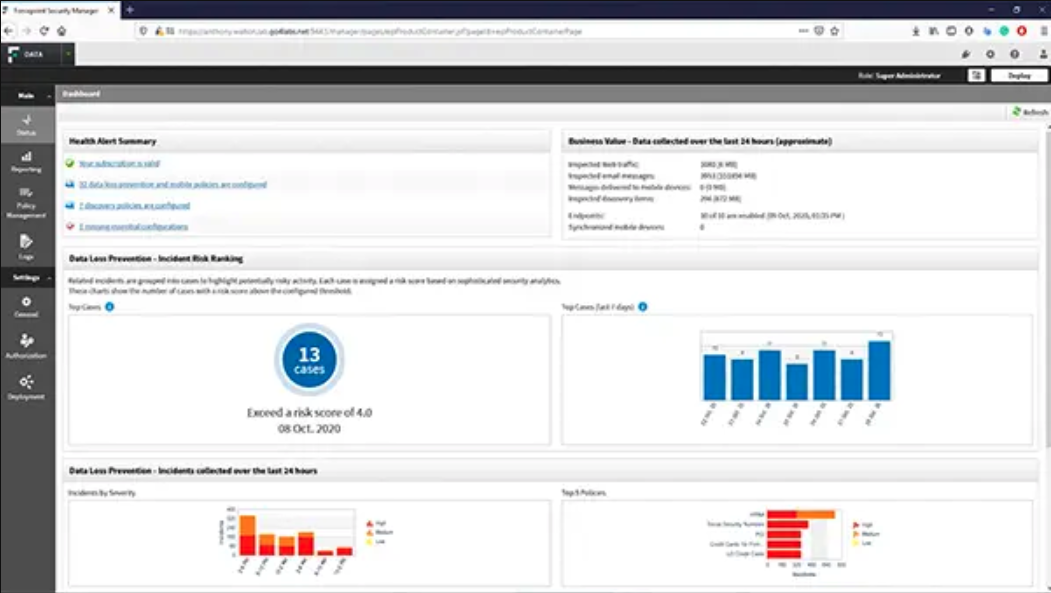
Data Loss Prevention DLP
Saiba Maisé a coleta de medidas usadas para evitar que os dados sejam perdidos, acessados por usuários não autorizados ou vazados, acidental ou propositalmente. A tecnologia DLP monitora os dados à medida que eles entram e saem de uma organização e impede a saída dos dados confidenciais.
Zero Trust Security
Saiba Maisé uma abordagem que presume que toda solicitação de acesso a dados, aplicativos ou outros recursos confidenciais é uma ameaça. Os princípios de Zero Trust visam a autenticar e validar continuamente o acesso de usuários e evitar que agentes maliciosos usem um único ponto de acesso para se mover lateralmente por uma rede segura.
Cloud App Security
Saiba Maisrefere-se à proteção de aplicativos e dados em ambientes de nuvem, além da proteção de dados que os fornecedores de nuvem oferecem a partir de uma perspectiva de infraestrutura. Isso é de crescente importância à medida que as organizações migram os dados e os ativos de data centers locais para a nuvem, e o uso de Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) prolifera.
Network DLP
É uma prática que monitora os dados em repouso, em movimento e em uso em toda a rede. Ele fornece mais aplicação de políticas para conformidade regulatória e oferece às organizações outra visão sobre a possível exfiltração de dados.
Email DLP
Saiba MaisÉ uma prática que monitora os dados em repouso, em movimento e em uso em toda a rede. Ele fornece mais aplicação de políticas para conformidade regulatória e oferece às organizações outra visão sobre a possível exfiltração de dados.
Endpoint DLP
Saiba Maisé a prática de proteger endpoints, ou seja, dispositivos de usuário final e interfaces como computadores, tablets e smartphones. Os endpoints criam pontos de entrada para uma rede empresarial para agentes maliciosos, e o risco aumenta quando os funcionários usam dispositivos pessoais não gerenciados para acessar os dados corporativos.
Os diferentes tipos de dados e como protegê-los
Embora uma empresa possa coletar, armazenar e processar informações em dezenas de formatos diferentes, tudo se resume a dois tipos de dados:
- Dados estruturados, que têm um modelo definido para exibição e são facilmente organizáveis e identificáveis. Os dados estruturados são frequentemente quantitativos, como números de previdência social, datas de aniversário ou transações.
- Dados não estruturados, que são menos definidos e podem vir em uma variedade de formatos. Os dados não estruturados são frequentemente qualitativos, como projetos, documentos ou imagens.

A partir daí, as organizações geralmente aplicam a segurança de dados a três áreas estratégicas:
- Big data: grandes volumes de informações coletadas de várias fontes para alimentar a modelagem preditiva, a publicidade direcionada, a manutenção preventiva e outras formas de análises de dados.
- Sensitive data: informações pessoais coletadas que contêm informações financeiras, médicas ou de outra forma de identificação pessoal.
- Business-critical data: informações confidenciais que definem a competitividade de uma empresa, como propriedade intelectual, ou são vitais para suas operações diárias, como métricas financeiras.
A segurança de dados terá uma aparência diferente dependendo do tipo de dados que a organização está buscando proteger. Geralmente, as empresas usarão um pacote de soluções para descobrir, classificar, priorizar, proteger e monitorar as interações com esses dados. Elas integrarão uma mistura de medidas preventivas, como mascaramento e criptografia de dados, com estratégias ativas, como prevenção contra a perda de dados para uma abordagem abrangente.
Segurança de Dados versus Privacidade de Dados
A segurança de dados e a privacidade de dados são conceitos estreitamente relacionados que têm obtenção de recursos, estratégias e requisitos tecnológicos separados.
A segurança de dados concentra-se na proteção dos dados contra acesso não autorizado, mantendo sua integridade e disponibilidade e impedindo que eles saiam da organização. Isso se estende a muitos aspectos da rotina diária de um usuário e, na Forcepoint, isso abrange, em grande parte, as atividades na nuvem, web, e-mail, rede e endpoint.
A privacidade de dados abrange as responsabilidades éticas e legais das organizações ao lidar com informações pessoais e respeitar os direitos de privacidade dos indivíduos. Essas responsabilidades mudam de país para país, mas geralmente estão ligadas às leis de privacidade de dados específicas do setor, como a Lei de Portabilidade e Responsabilidade de Seguros de Saúde (HIPAA), ou a regulamentos amplos de dados, como o Regulamento Geral de Proteção de Dados (GDPR).
A segurança de dados e a privacidade de dados geralmente estão associados devido aos requisitos de relatórios normativos. Na Forcepoint, isso pode ser aplicado pelo software de DLP na forma de políticas de segurança de dados. Ambos os aspectos são cruciais para manter a confiança com clientes e reguladores.
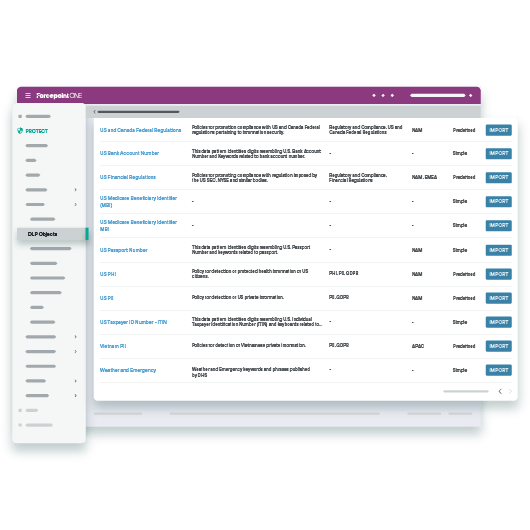
Os principais aspectos da privacidade de dados incluem:
- Obtenção do consentimento antes de coletar ou usar dados pessoais
- Coleta e processamento de dados apenas para fins específicos
- Coleta e manutenção apenas da quantidade mínima de dados pessoais necessários
- Remoção ou criptografia de identificadores pessoais para anonimizar os dados
- Respeito dos direitos dos indivíduos de acessar e corrigir seus dados pessoais ou restringir seu uso
- Notificação a indivíduos e autoridades sobre violações de dados
Devido à quantidade de dados que as organizações produzem e pelos quais são responsáveis, é fundamental uma abordagem abrangente para protegê-los. Práticas proativas, como classificação de dados, descoberta de dados, criptografia de dados e DLP são úteis para priorizar, proteger e monitorar os dados.
Regulamentos da Segurança de Dados
Os órgãos governamentais em todo o mundo implementam os regulamentos de segurança de dados para garantir que as organizações tomem as devidas precauções para coletar, armazenar e usar informações confidenciais com segurança.
Qualquer estratégia de segurança de dados viável deve incluir a capacidade de garantir e demonstrar a conformidade com os regulamentos pertinentes. Alguns dos principais regulamentos que podem afetar suas políticas de dados são:
LGPD
A Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD): o Brasil está sujeito a este regulamento que rege a coleta e o uso de dados pessoais, que também serve como modelo para muitas leis de privacidade que surgem em todo o mundo, como o GDPR na Comunidade Européia
HIPAA
A Lei de Portabilidade e Responsabilidade de Seguros de Saúde (HIPAA): os registros de saúde nos Estados Unidos são regidos pela HIPAA, que agora pode ser aplicada de forma mais eficaz por meio da Lei de Tecnologia da Informação em Saúde para Saúde Econômica e Clínica (HITECH) de 2009.
PCI DSS
Padrão de Segurança de Dados da indústria de cartões de pagamento (PCI DSS): esse padrão foi desenvolvido pelas principais empresas de cartão de crédito e destina-se a garantir a transferência segura de dados de cartão de crédito e evitar fraudes.
Dependendo dos países e setores em que você opera, existem inúmeros regulamentos que podem afetar sua abordagem para a segurança de dados e a privacidade de dados.
Algumas organizações recorrerão ao software de DLP para garantir a conformidade. O Forcepoint DLP oferece políticas de segurança de dados out-of-the-box que são mapeadas para seus regulamentos de privacidade de dados locais — enquanto outros fornecem um roteiro, mas exigem mais trabalho para fazer com que sejam mapeados corretamente.
Estar ciente de todos esses e ter um plano de conformidade ativo para cada um deve ser um elemento essencial das operações de segurança de qualquer organização.
Desafios e tendências da segurança de dados
A segurança de dados tem sido uma importante prioridade para as organizações durante a maior parte dos últimos 30 anos.
Desde a primeira transação de comércio eletrônico e a introdução de portais de saúde na década de 1990, até a proliferação de Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) e mídias sociais na década de 2010, as empresas de todos os setores têm coletado e processado regularmente dados que variam nas centenas de terabytes.
As informações confidenciais, que vão desde a previdência social e números de cartão de crédito até filmes ou videogames não lançados, são um importante alvo para os agentes de ameaças devido ao seu valor no mercado ilegal e à potencial interrupção dos negócios.
Não é novidade que os países em todo o mundo tenham se mobilizado rapidamente para implementar regulamentos projetados para conter os dados que as empresas podem coletar, aplicar um melhor tratamento desses dados e garantir que as organizações estejam protegendo esses dados com o máximo de atenção possível.
Essas tendências levaram aos seguintes desafios de segurança de dados que serão generalizados ao longo de 2023 e além:

Proteção contra ameaças
Engenharia social, malware e ataques à cadeia de suprimentos tornaram-se comuns e uma importante fonte de violações de dados. Na verdade, a IBM relata que 52% das violações são causadas por um ataque malicioso. Phishing, ransomware e ameaças de dia zero colocam em risco dados como informações de identificação pessoal ou propriedade intelectual.
Ambientes de trabalho híbridos
Os aplicativos de nuvem acionam as empresas nos dias de hoje. Embora permitam que os funcionários trabalhem de qualquer lugar, os aplicativos de nuvem também criam novos riscos para a segurança de dados organizacionais. É cada vez mais difícil para as empresas obter visibilidade dos dados e seu uso nessas plataformas e controlar o acesso apenas para aqueles que são confiáveis. Como resultado, muitos vazamentos e violações de dados são o resultado da segurança de dados deficiente na nuvem.
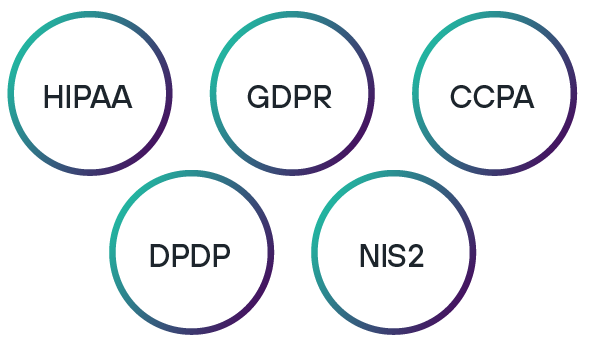
Exame regulatório
O Regulamento Geral de Proteção de Dados (GDPR) na Europa e a Lei de Privacidade do Consumidor da Califórnia (CCPA) nos EUA foram o início de um dilúvio de problemas de privacidade e segurança de dados que se transformaram em uma conformidade obrigatória, assim como o LGPD no Brasil. As organizações devem lidar com as responsabilidades regulatórias concorrentes que ditam como devem armazenar e proteger os dados — e comprovar aos auditores que estão mantendo a conformidade. Com mais leis de privacidade, como a lei de Proteção de Dados Pessoais Digitais (DPDP) na Índia e a Diretiva NIS2 na Europa agora a caminho, as empresas devem continuar a investir em segurança de dados para evitar a não conformidade.

Pilha de tecnologia quebrada
À medida que as organizações enfrentam mais ameaças de cibersegurança e a superfície de ataque cresce ao longo dos anos, as pilhas de tecnologias de segurança crescem com ela. Há milhares de fornecedores que vendem soluções de nicho que nem sempre interagem de forma honesta uns com os outros, criando alertas falsos que consomem o tempo das equipes de segurança que já estão esgotadas. Some-se a isso a criação e a manutenção de políticas de segurança de dados, que continua a se expandir com a superfície de ataque e é fácil ver por que as ferramentas de segurança unificadas e as políticas de segurança de dados dirigem-se para as médias e grandes empresas.
O cenário de ameaças à Segurança de Dados
O cenário de ameaças está constantemente mudando em resposta às últimas inovações, tanto de profissionais de segurança quanto de agentes maliciosos, o que significa que práticas de segurança de dados sólidas não devem se resumir à simples aplicação de estratégias que funcionaram no passado.
As ameaças cibernéticas, como ransomware e malware capturam as manchetes por causa dos danos financeiros e operacionais que causam. Inúmeras organizações em todo o mundo admitiram o pagamento de um resgate para colocar seus dados e sistemas novamente online, e outras, como o NHS, sentiram consequências por até mesmo um dia de tempo de inatividade.
Mas há outras ameaças à segurança de dados menos óbvias. Os intervalos abertos na AWS são uma origem corriqueira para vazamentos de dados, quando os profissionais removem os controles de segurança durante as migrações para facilitar as coisas para si mesmos, deixando as instâncias desprotegidas e vulneráveis a vazamentos de dados.
Agora, com a popularidade dos serviços de nuvem como o Google Docs, Slack e inúmeras outras ferramentas de produtividade, as organizações têm ainda mais riscos para cobrir em sua estratégia de segurança de dados. As equipes de TI não só precisam garantir que os fornecedores de SaaS mantenham sua infraestrutura segura, mas precisam obter visibilidade sobre os dados com os quais os funcionários estão trabalhando nessas plataformas. Esse risco é amplificado com o surgimento da IA generativa, que pode aprender com os dados que estão sendo compartilhados.
Riscos da Segurança de Dados
Existem incontáveis tipos de riscos à segurança de dados e a lista só fez crescer com novas técnicas de hacking e engenharia social emergindo continuamente.
Embora os grandes ataques cibernéticos tendam a ganhar as manchetes, nem todos os riscos à segurança de dados são produto de ação maliciosa intencional. Na verdade, os principais riscos podem resultar de comportamentos não intencionais que fazem com que os dados confidenciais sejam liberados em espaços não protegidos, onde podem ser roubados ou explorados.

As categorias de risco à segurança de dados incluem:
- Exfiltração de dados: esse conceito amplo refere-se a qualquer movimento não autorizado de dados, seja acidental ou malicioso. E-mails de saída, downloads para dispositivos inseguros e uploads para dispositivos externos são algumas das ações que podem levar à exfiltração de dados.
- Vazamento de dados: sob o signo da exfiltração de dados, o vazamento de dados refere-se mais especificamente à transmissão não autorizada de dados de dentro de uma organização para um destino ou destinatário externo. O termo pode ser usado para descrever a transferência eletrônica ou física de dados. As ameaças de vazamento de dados geralmente ocorrem pela web e por e-mail, mas também podem acontecer por meio de dispositivos de armazenamento de dados móveis, como notebooks e chaves USB que são perdidos, roubados ou intencionalmente usados para transferir informações confidenciais.
- Phishing: o phishing refere-se ao uso fraudulento de comunicações eletrônicas para enganar e tirar proveito de indivíduos-alvo. O e-mail é a forma tradicional de phishing, mas cada vez mais os invasores usam caminhos adicionais, como SMS, mídias sociais e chamadas telefônicas. O phishing envolve o uso de engenharia social para manipular as vítimas para que elas realizem ações específicas — como clicar em um link malicioso ou baixar um anexo — ou fornecer informações confidenciais, como credenciais de conta. Há uma lista crescente de abordagens de phishing especializadas — spear phishing, clone phishing e caça à baleia são alguns — à medida que os invasores constantemente criam novas estratégias.
Os riscos à segurança de dados são uma preocupação para todos, desde as maiores empresas até as pequenas organizações, e as consequências de uma violação podem ser devastadoras. É uma importante razão pela qual tantas organizações recorrem à Forcepoint em busca de ajuda para proteger seus dados.
Para se ter uma noção da dimensão do problema, em 2022 houve um total de mais de 1 bilhão de registros expostos e mais de US$ 5,3 bilhões em perdas e multas incorridas. Além do impacto financeiro de curto prazo dos riscos à segurança de dados, as violações frequentemente levam à perda de confiança do cliente e do valor da marca que podem comprometer a viabilidade das organizações no longo prazo.
Como proteger os dados
Soluções de Segurança de Dados
As organizações precisam empregar soluções de segurança de dados especificamente desenvolvidas para mitigar os riscos. Mas nem todas as soluções são adequadas para todos, como é a Forcepoint.
As estratégias de segurança de dados devem incorporar várias soluções para fornecer todos os recursos necessários na proteção contra ameaças modernas e garantir a administração responsável de dados confidenciais. Vários fatores distinguem as soluções de segurança de dados da Forcepoint de concorrentes de baixo desempenho.
As organizações devem ser capazes de cobrir algumas atividades diferentes com suas soluções de segurança de dados. Eles incluem:
- Descobrir dados que são usados ativamente e redundantes, obsoletos ou triviais.
- Classificar os dados para obter uma imagem precisa dos dados que a organização tem e avaliar sua relevância.
- Priorizar os dados que precisam ser protegidos com base em uma variedade de critérios.
- Proteger os dados por meio de controles de segurança de dados robustos.
- Monitorar o fluxo de dados em toda a empresa para garantir uma cobertura abrangente.
Tecnologias de Segurança de Dados
Local versus SaaS
A decisão sobre quais tecnologias de segurança de dados adotar deve começar perguntando como a organização precisa que elas sejam hospedadas.
As soluções locais são hospedadas internamente e sua manutenção pode ser econômica após o preço inicial de implementação. Uma solução de Software-as-a-Service (Saas) é hospedada por um provedor terceirizado e armazena os dados em um data center seguro na nuvem. As soluções de SaaS são mais escaláveis para organizações em crescimento e não são vulneráveis à perda de dados catastrófica se um data center interno for danificado por um desastre, como incêndio ou inundação.
As soluções de segurança de dados da Forcepoint podem ser implantadas de várias maneiras para atender às necessidades de todas as empresas.
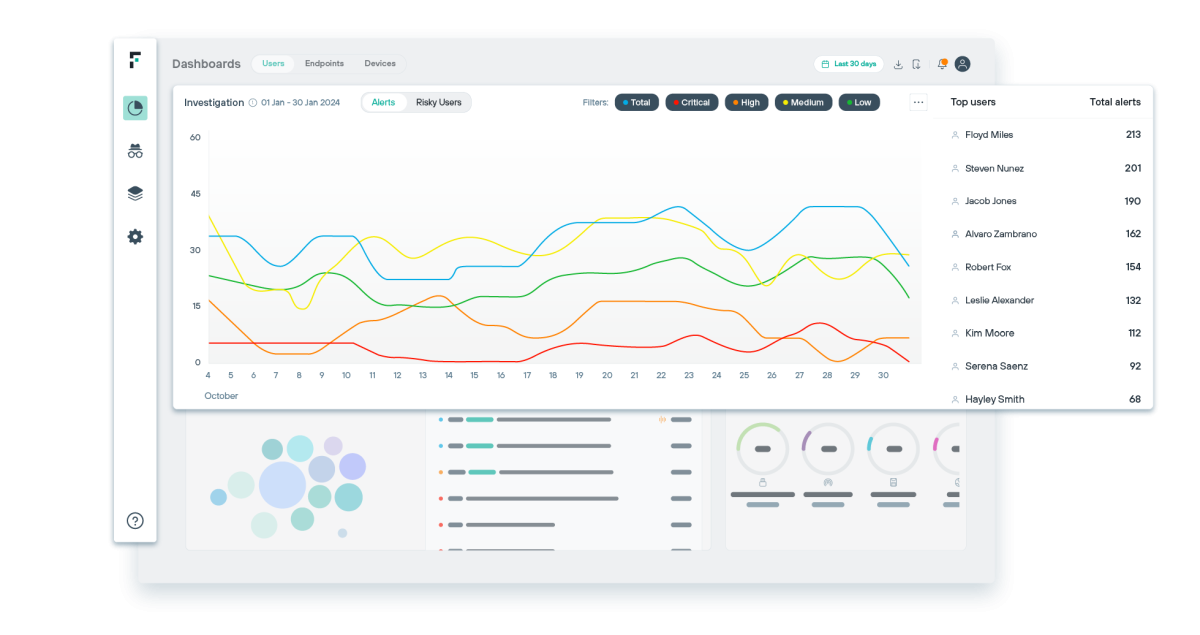
Forcepoint ONE Data Security
Forcepoint ONE Data Security é um DLP SaaS nativo de nuvem que permite que as empresas protejam informações confidenciais e apliquem conformidade por meio de uma plataforma. Ele simplifica a segurança de dados moderna por sua capacidade de::
- Unifique o gerenciamento de políticas em nuvem, web, e-mail e endpoint
- Crie e provisione políticas em minutos usando uma biblioteca de mais de 1.700 classificadores e modelos
- Monitore e corrija incidentes em tempo real por meio da aplicação de políticas, incluindo a Risk-Adaptive Protection integrada
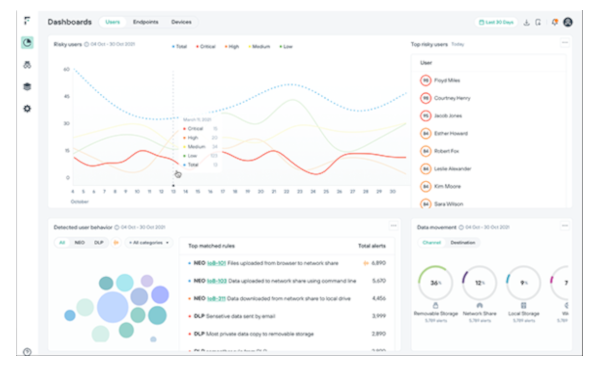
Risk-Adaptive Protection
O Forcepoint Risk-Adaptive Protection aplica uma abordagem centrada no comportamento à segurança de dados, examinando como os usuários interagem com os dados para entender melhor sua intenção. Isso permite às organizações:
- Manter a produtividade permitindo que usuários de baixo risco trabalhem desimpedidos
- Minimizar os falsos positivos para evitar sobrecarregar os profissionais de segurança
- Desbloqueie recursos abrangentes de monitoramento em mais de 100 Indicadores de Comportamentos (IOBs)
- Limitar automaticamente o acesso quando os usuários exibem comportamentos não característicos que podem indicar comprometimento
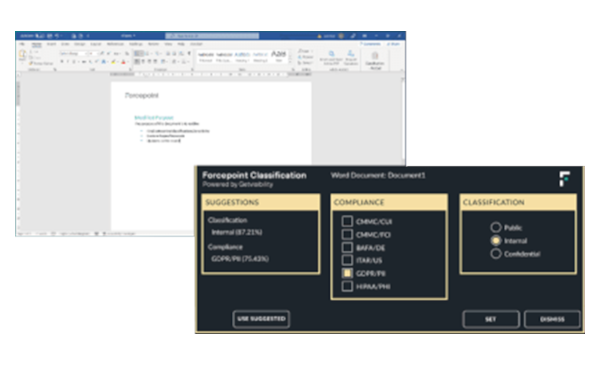
Data Classification
O Forcepoint Data Classification usa o Machine Learning (ML) e a inteligência artificial (IA) para classificar os dados não estruturados com mais precisão, mantendo a segurança das informações críticas e aumentando a produtividade. Com a tecnologia de ponta dos modelos de IA, ele pode:
- Determinar com precisão e eficiência como os dados devem ser classificados, em escala
- Englobar a mais ampla gama de tipos de dados do setor para impulsionar a eficiência e simplificar a conformidade
- Ser implantado com perfeição e sem treinamento de usuários, integrando-se ao Forcepoint Enterprise DLP para permitir que as organizações selecionem os requisitos e critérios para classificação de dados
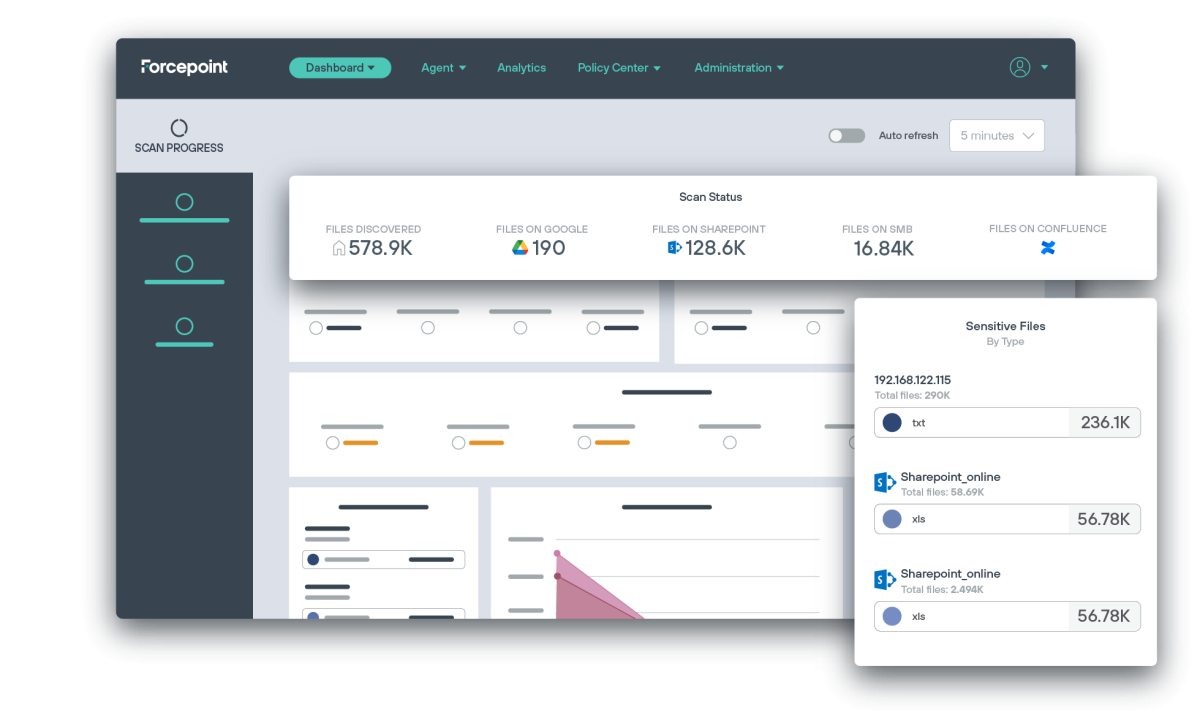
Data Security Posture Management
O Forcepoint Data Security Posture Management (DSPM), desbloqueia o controle total e a visibilidade sobre os dados da empresa. Descubra, classifique e organize os dados por meio de automação e machine learning com tecnologia de IA para impedir violações e aplicar conformidade.
- Digitalize até 300 arquivos por segundo e dimensione até um milhão por hora por meio de sites de armazenamento em nuvem e on-premises.
- Descubra o risco de dados, como duplicação de dados, dados obscuros, armazenamento ou permissões de arquivos incorretos e corrija em tempo quase real.
- Forneça exatidão de classificação altamente precisa por meio de inteligência artificial e use machine learning para melhorar continuamente a exatidão do modelo.
DLP for Email
O Forcepoint DLP for Email permite que as empresas estendam as políticas de DLP para o e-mail de saída — a fonte mais comum de perda de dados. Isso oferece:
- Cobertura de mais de 1.700 classificadores e modelos de políticas pré-criados
- Controle sem agente no M365 Exchange, Google Workspace e outras plataformas
- Funcionalidade nativa e capacidades aprimoradas de administração de e-mail
Comparar e avaliar as ferramentas de segurança de dados
Há muitos casos de uso exclusivos em que as organizações recorrem à DLP e outras soluções de segurança de dados para solucionar. Embora analistas como o Forrester, Gartner e Radicati divulguem regularmente análises de mercado para manter os compradores atualizados sobre as inovações mais recentes, um gráfico de comparação de funcionalidades pode ser igualmente valioso.
A Forcepoint desenvolveu um gráfico de comparação de funcionalidades que contrasta a funcionalidade do Forcepoint DLP com a de fornecedores bem conhecidos, como Symantec, Trellix e Microsoft.

Descubra como você pode proteger seus dados facilmente em todos os lugares.
Como implementar a Data Security Everywhere
Como a segurança de dados precisa de uma abordagem abrangente, a capacidade de unificar políticas, gerenciamento e relatórios é fundamental. Introdução: Data Security Everywhere
Data Security Everywhere is Forcepoint’s answer, allowing people to work anywhere in the world while accessing data everywhere it resides, safely.
Os cinco passos para o Data Security Everywhere
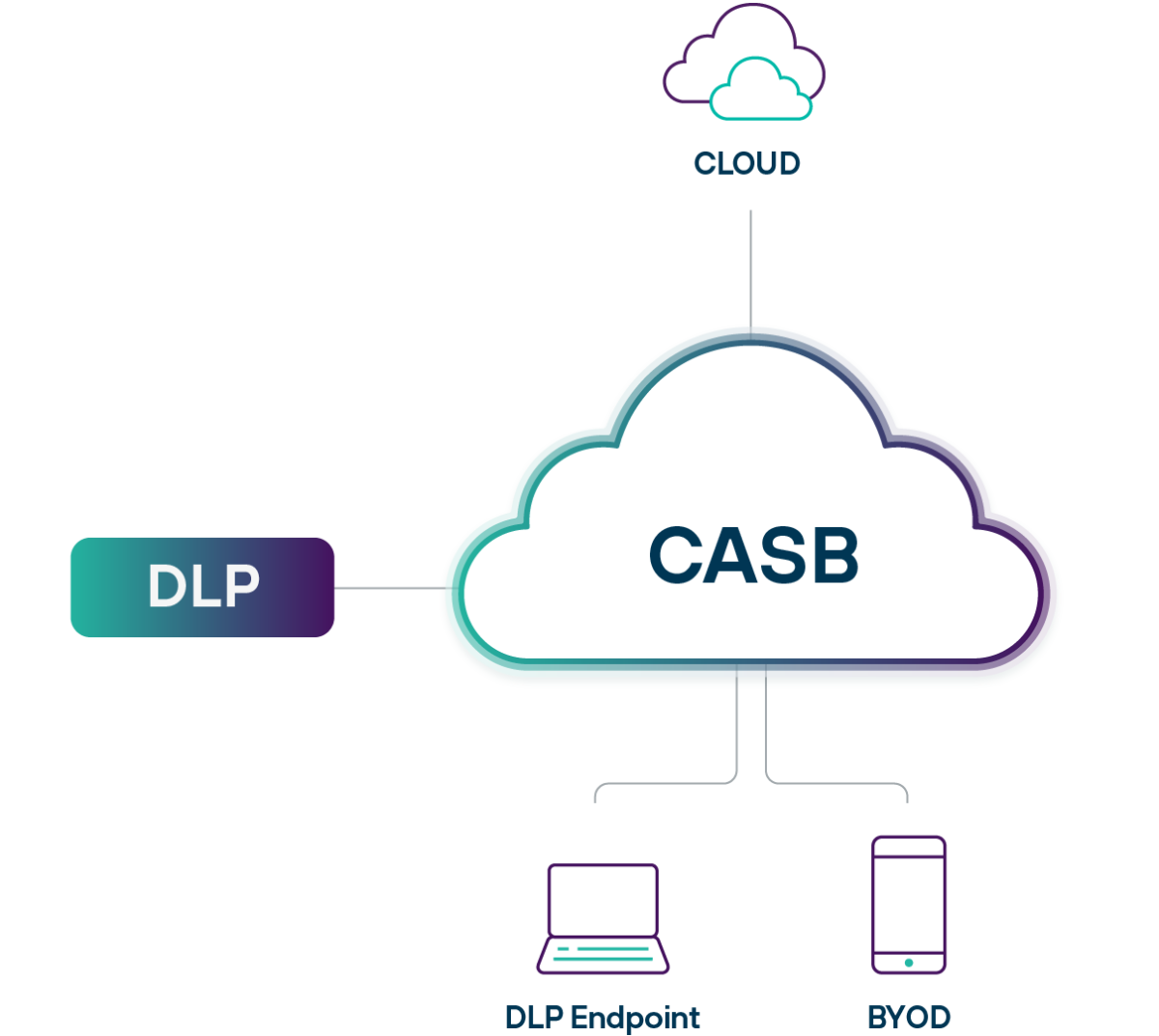
Unifique a Nuvem, o Endpoint e a Proteção de Dados no BYOD
O Forcepoint DLP e o Forcepoint ONE CASB permitem que as empresas escalem o DLP para usuários em todos os lugares e unifiquem a proteção de dados de nuvem, endpoint e BYOD. Aproveite a maior coleção de classificadores e políticas pré-criadas do setor e replique as políticas com apenas alguns cliques.
- Estenda as políticas de DLP para mais de 800.000 aplicativos de nuvem em dispositivos gerenciados e não gerenciados
- Aplique políticas em dispositivos não gerenciados e dentro de aplicativos da web não gerenciados
- Elimine vários DLPs e o processo meticuloso de sincronizar manualmente as políticas entre eles
Extend DLP policies to over 800,000 cloud applications on both managed and unmanaged devices
Enforce policies on unmanaged devices and within unmanaged web apps
Eliminate multiple DLPs and the pain-staking process of manually syncing policies between them
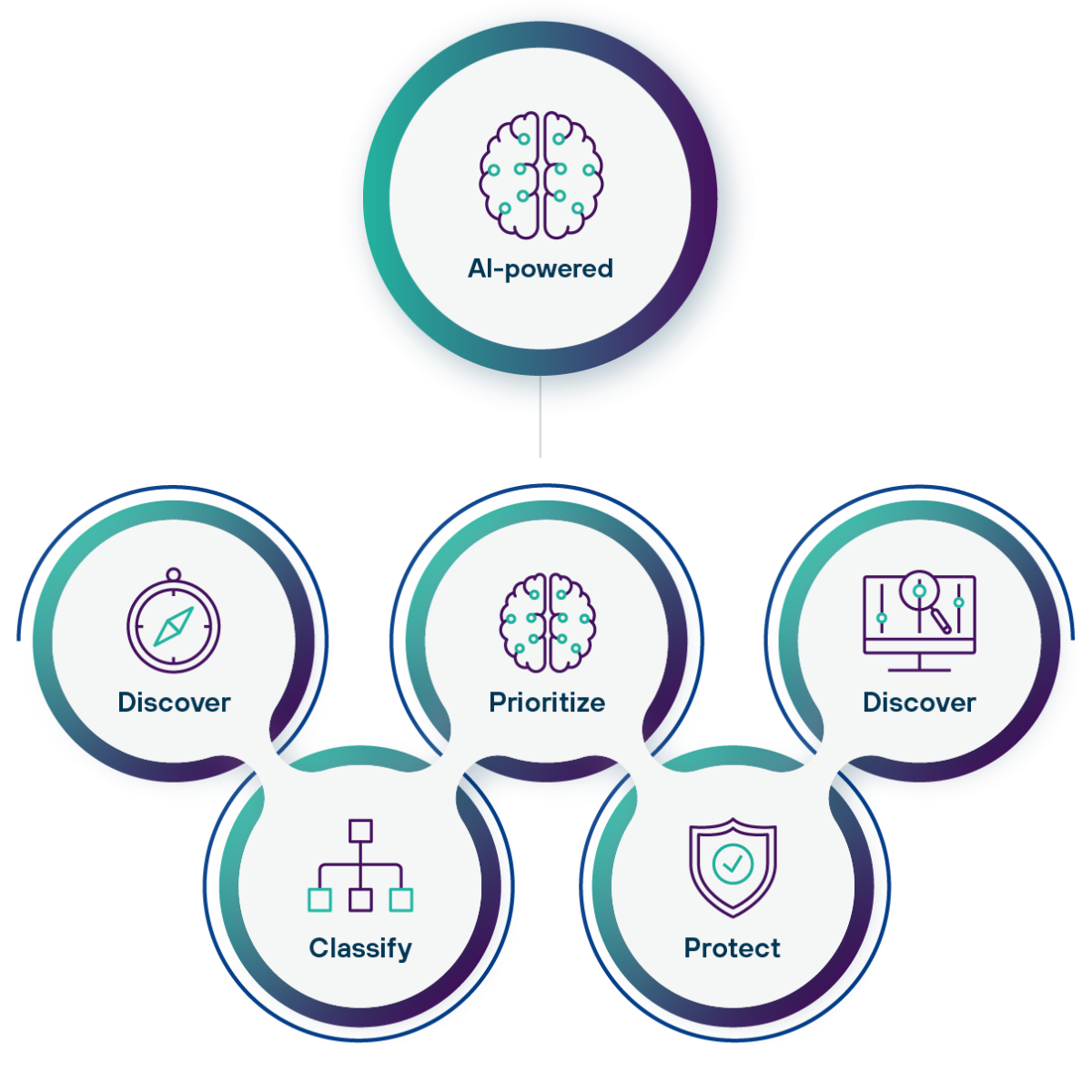
Descoberta e classificação de dados com tecnologia de IA
Você não pode proteger o que não consegue ver. Descubra e proteja dados não estruturados e classifique e proteja dados confidenciais em toda a empresa usando automação com tecnologia de IA para obter melhor visibilidade e controle, reduzir o risco e simplificar a conformidade.
- Localize e classifique os dados com precisão e eficiência com machine learning e inteligência artificial
- Categorize os dados usando mais de 70 campos e dentro de mais de 50 tipos de arquivos
- Visualize permissões de usuários, locais de arquivos e muito mais para evitar incidentes e implementar Zero Trust
Locate and classify data accurately and efficiently with machine learning and artificial intelligence
Categorize data using 70+ fields and within 50+ file types
View user permissions, file locations and more to prevent incidents and implement Zero Trust
Automatize a segurança de dados com base no comportamento de risco
Automaticamente adapte as políticas com base no comportamento de risco do usuário para impedir ameaças internas e evitar violações ou vazamentos de dados em tempo real. O Risk-Adaptive Protection permite que as empresas desbloqueiem a produtividade e reduzam alertas falsos com o controle de políticas dinâmico.
- Atribua ações desde autoaprendizagem até o bloqueio com base em atividades de risco
- Ajuste as políticas em tempo real com base no contexto do comportamento do usuário
- Reduza os alertas de falso positivo sem prejudicar os funcionários
Assign actions from self-learning to blocking based on risky activities
Adjust policies in real time based on context of user behavior
Reduce false positive alerts without limiting employees
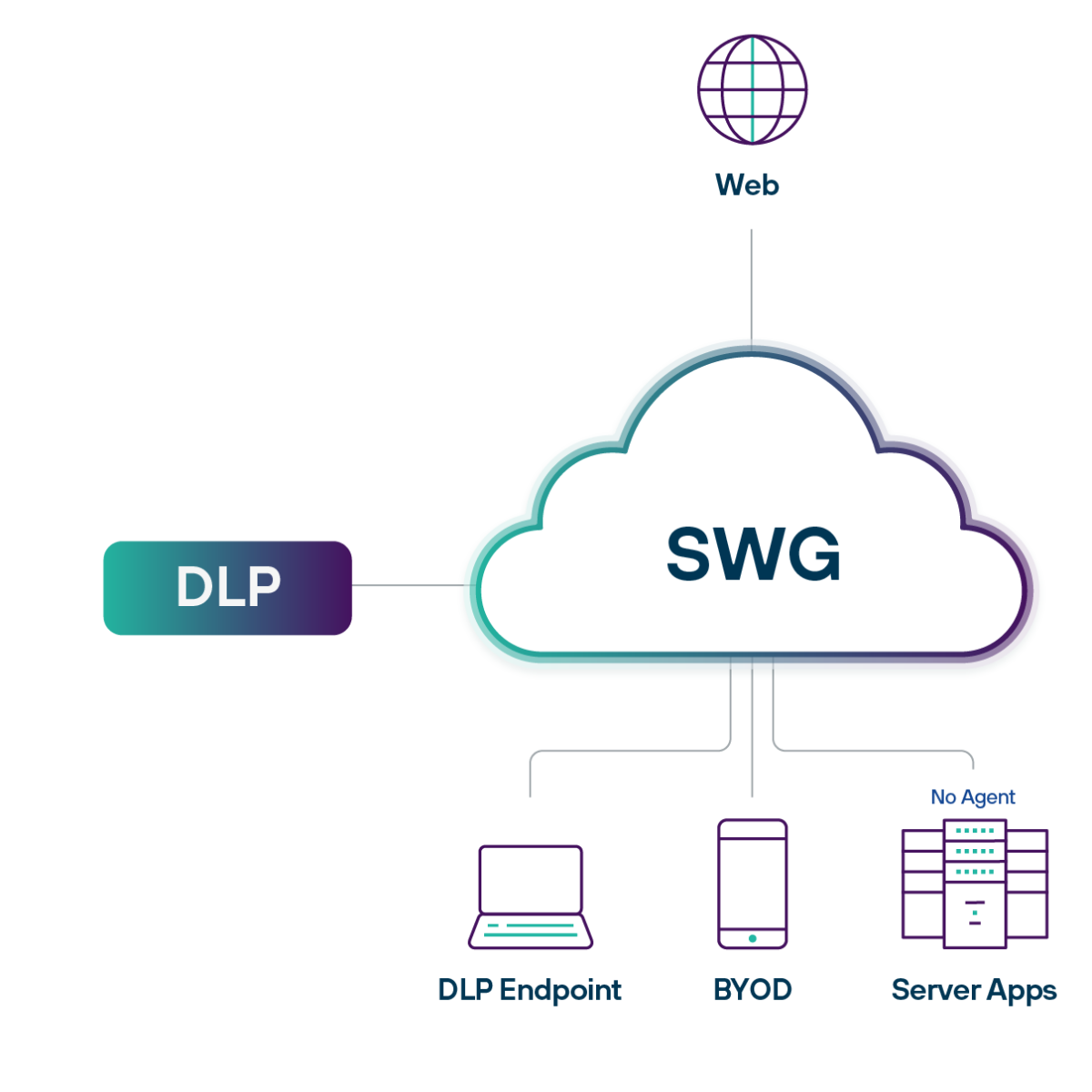
Proteja usuários e dados na Web
A web apresenta dois perigos para os dados: ransomware e exfiltração. Mantenha os usuários e os dados seguros ao evitar ataques de malware conhecidos e desconhecidos, bem como interromper o upload de dados confidenciais para o armazenamento e aplicativos da web.
- Impeça os ataques de malware abrindo sites potencialmente de risco em contêineres
- Inspecione e controle os dados carregados para o armazenamento e aplicativos da web
- Elimine várias ferramentas de segurança de dados e a sincronização manual de políticas entre elas
Stop malware attacks by opening potentially risky websites in containers
Inspect and control data uploaded to web storage and applications
Eliminate multiple data security tools and the manually policy syncing needed between them
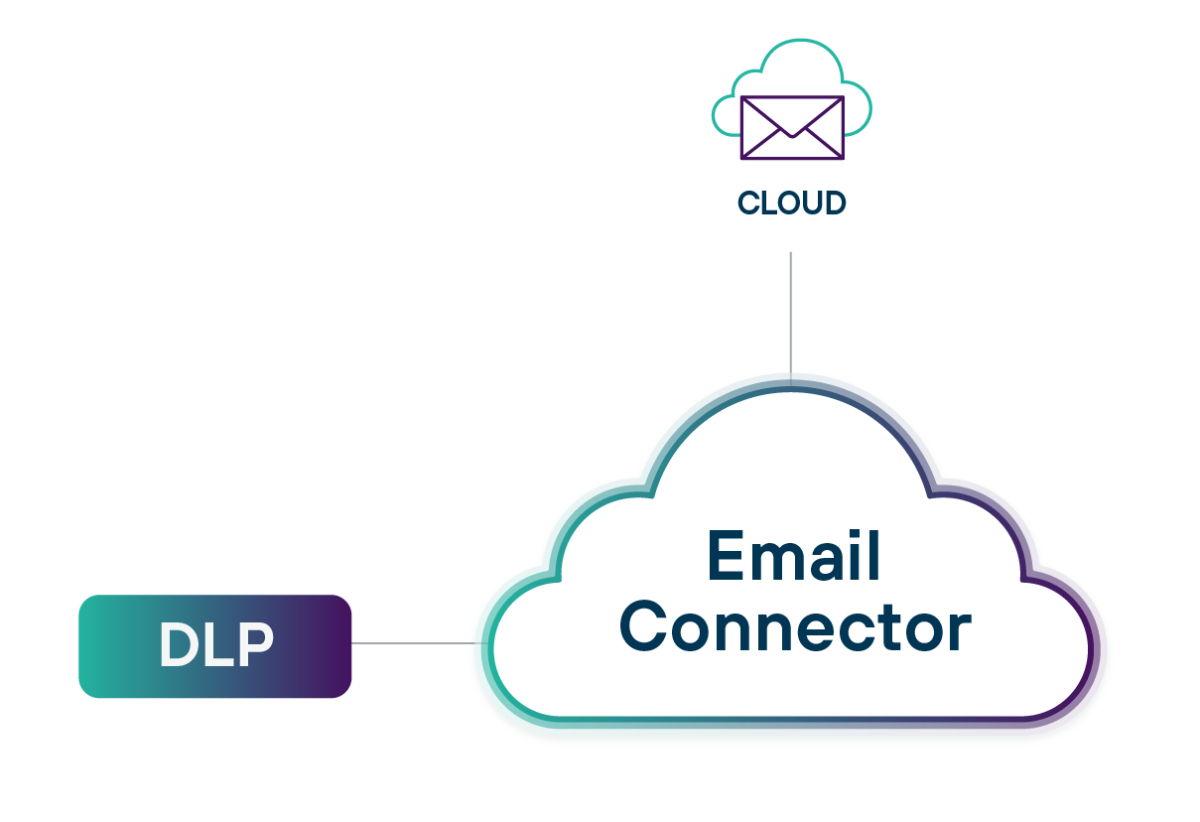
Evite o roubo de dados em e-mails enviados
O e-mail é a fonte número 1 de exfiltração de dados. Estenda as políticas de DLP para o e-mail de saída para impedir que dados confidenciais saiam da organização, enquanto melhora as funcionalidades e capacidades nativas da administração de e-mails existente.
- Implemente em minutos no M365 Exchange, Google Workspace e outras plataformas de multiplicadores
- Obtenha visibilidade e controle sobre quais dados podem ser compartilhados por e-mail
- Aprimore recursos como quarentena, criptografia e muito mais
Deploy in minutes on M365 Exchange, Google Workspace, and other popular platforms
Get visibility and control over what data can be shared via email
Enhance capabilities such as quarantine, encryption and more
Melhores práticas da Segurança de Dados
Melhores práticas para proteger os dados em todos os lugares
Com o Forcepoint DLP, as organizações podem unificar o gerenciamento de políticas a partir de uma implantação local em aplicativos de nuvem, web e privados com apenas alguns cliques. Isso torna possível gerenciar vários canais com uma única política e estender rapidamente as políticas para dispositivos gerenciados e não gerenciados, economizando tempo e garantindo a segurança de dados abrangente. O acesso ao banco de dados da Forcepoint com mais de 1.600 classificadores de DLP também oferece aplicação de políticas granular para aplicativos web, nuvem e privados, para que você possa proteger os dados em todos os lugares onde os usuários os acessam.
O gerenciamento da segurança de dados em todos esses canais é otimizado quando você aproveita o Forcepoint ONE Data-first SASE, uma plataforma de segurança completa, nativa da nuvem. O Forcepoint ONE permite uma abordagem modular para a segurança de dados, permitindo que as organizações comecem implantando o que mais precisam e, posteriormente, adicionem mais soluções ao longo do tempo. O gerenciamento de todas as funções de segurança por meio de um único painel facilita o monitoramento e o controle dos fluxos de dados em todos os canais. O Forcepoint ONE também inclui as plataformas de análises do Insights, que visualiza a criação de valor econômico em tempo real para quantificar os benefícios do seu programa de segurança de dados.
O Forcepoint DLP e o Forcepoint ONE também podem ajudar as empresas a usar chatbots de IA generativa como o ChatGPT e Bard, sem o risco de vazamento de dados críticos. As organizações podem definir políticas sobre quem tem acesso à IA generativa, evitar o upload de arquivos restritos e bloquear a colagem de informações confidenciais. Isso libera os trabalhadores para aproveitar os ganhos de produtividade oferecidos pela IA sem perder o controle da propriedade intelectual ou outros dados críticos.
Analistas sobre ferramentas de Segurança de Dados líderes do setor
Não há duas soluções de segurança de dados iguais. Muitos profissionais recorrem a analistas do setor, como o Gartner, Forrester e Radicati, para obter orientação sobre os benefícios e desvantagens de cada fornecedor de segurança de dados.
O melhor lugar para começar é com publicações amplamente reconhecidas que examinam o estado atual do mercado e identificam quais são as principais soluções. Dê uma olhada:
Case Studies
Depending on your industry, company size or industry, data security requirements will vary widely from one company to another.
To see how real customers are putting Forcepoint solutions to work to protect data everywhere, examine these case studies selected from the collection on our website:
Perguntas frequentes
Quais são as melhores práticas para a segurança de dados?
As melhores práticas de segurança de dados exigem uma abordagem abrangente com base em um pacote integrado de soluções.
Adote uma abordagem abrangente para proteger os dados que envolvem:
- Descobrir os dados que precisam de proteção, do endpoint à nuvem.
- Classificar as informações confidenciais para descobrir o risco oculto.
- Priorizar uma postura de segurança de dados forte por meio de relatórios exaustivos.
- Proteger os dados em tempo real com políticas de DLP robustas.
- Monitorar as interações com os dados para manter a conformidade.
Embora a DLP seja a tecnologia de segurança de dados mais comum, ela não é a única solução que pode ter um impacto poderoso. Outras soluções de melhores práticas a incorporar incluem:
- Uma solução que fornece visibilidade dos dados — especialmente informações redundantes, obsoletas ou triviais — em toda a organização.
- A capacidade de classificar os dados por públicos, sensíveis ou confidenciais e rastrear seu uso em toda a empresa.
- Proteção de políticas adaptáveis a riscos, que usa o contexto para delinear as interações seguras a partir das interações de risco e ajusta as políticas adequadamente.
Quais são as soluções e ferramentas de segurança de dados disponíveis?
Há dezenas de soluções e ferramentas de segurança de dados disponíveis para as empresas. Ao considerar quais soluções adotar, esforce-se para manter controles fortes em torno do acesso a aplicativos onde os dados residem. Eles incluem:
- Cloud security, como um Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB).
- Web security, como um Secure Web Gateway (SWG).
- Email security, como DLP para e-mail.
- Endpoint security, como a DLP.
Como medir e demonstrar a eficácia da sua estratégia de segurança de dados?
Uma estratégia de segurança de dados eficaz fornecerá uma ampla cobertura das políticas de DLP, evitará alertas falsos positivos e realizará auditorias detalhadas sobre incidentes para ver como os funcionários estão respondendo ao longo do tempo a quaisquer mudanças em sua abordagem.
As soluções de segurança de dados da Forcepoint oferecem às equipes relatórios detalhados por meio de um painel fácil de usar. Algumas tecnologias, como as da plataforma Forcepoint ONE, beneficiam-se dos relatórios unificados por meio do Forcepoint Insights.
Como implementar uma política de segurança de dados?
As políticas de segurança de dados podem ser configuradas e mantidas por meio de uma solução de DLP. Assista a “A Day in the Life of a Forcepoint DLP Administrator” para ver como é simples criar uma política dentro do Forcepoint DLP.
Aqui está um breve guia passo a passo sobre how to build a DLP policy no Forcepoint DLP:
- Descubra e classifique seus dados.
- Navegue até o nível de política correto com base em como você deseja que eles sejam acionados.
- Inicie uma nova política do zero ou usando um modelo predefinido.
- Nomeie a política e adicione classificadores para quais dados e interações ela deve monitorar.
- Determine a gravidade que os incidentes acarretariam e quaisquer ações resultantes.
- Identifique fontes a monitorar, como o Active Directory ou a rede.
- Determine os destinos a serem monitorados, como endpoint, web ou nuvem.
Como instruir a equipe sobre segurança de dados?
O treinamento de conscientização sobre a segurança de dados é fundamental para instruir a equipe sobre a higiene e as melhores práticas da segurança de dados, bem como as ameaças cibernéticas que colocam as informações confidenciais em risco.
Com o Forcepoint DLP, os administradores podem trabalhar o treinamento de conscientização sobre a segurança de dados em suas políticas de DLP como uma resposta a um incidente. Se um funcionário tentar anexar uma lista de números de previdência social a um e-mail, por exemplo, as equipes de segurança de dados podem aplicar um pop-up explicando por que isso não é permitido, qual seria o melhor método e fornecer mais detalhes sobre melhores práticas de higiene de dados.
Como conduzir uma auditoria de segurança de dados?
As empresas devem primeiro saber quais informações confidenciais elas têm e onde essas informações estão localizadas antes de realizar uma auditoria de segurança de dados. O Forcepoint Data Visibility e o Forcepoint Data Classification ajudam as organizações a obter a visibilidade dos dados em todos os lugares da organização e a classificar esses dados com base na gravidade e risco, respectivamente.
As empresas podem realizar auditorias de segurança de dados contínuas revisando os incidentes rastreados em sua DLP. Cada incidente é registrado, independentemente de sua gravidade e resposta. Com o tempo, os administradores podem usar as auditorias para detectar padrões, ajustar a cobertura de políticas de DLP e, claro, manter a conformidade com uma série de regulamentos.
Como gerenciar a segurança de dados na nuvem?
O gerenciamento da segurança de dados na nuvem se resume a ser capaz de proteger o acesso e manter a visibilidade dos dados que são usados na nuvem.
A proteção do acesso tem dois elementos: permitir que as pessoas em qualquer lugar acessem aplicativos de nuvem em todos os lugares e garantir que apenas as pessoas que explicitamente precisam usar esses aplicativos tenham acesso a eles.
Um Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) é comumente usado para fornecer acesso seguro a aplicativos de nuvem. O Forcepoint ONE CASB inclui controles de segurança de dados fortes para gerenciar os dados que as pessoas usam no Slack, Dropbox e outras plataformas comuns.
O Forcepoint ONE é uma plataforma Zero Trust que permite que as organizações apliquem o princípio de menor privilégio. Isso limita o número de pessoas com permissão para acessar os dados em qualquer aplicativo de nuvem, mantendo as potenciais ameaças internas ou agentes de ameaças longe de acessar essas informações confidenciais.
Como o SASE melhora a segurança de dados em um ambiente de nuvem?
O Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) reúne os serviços de segurança na borda com as soluções de rede. No entanto, a segurança de dados é intrínseca ao SASE, pois os serviços seguros que se enquadram no SASE — Cloud Access Security Broker, Secure Web Gateway e Zero Trust Network Access — todos convergem sob uma importante funcionalidade: proteger o acesso a recursos críticos para os negócios.
Quando o Forcepoint ONE CASB, o Forcepoint ONE SWG e o Forcepoint ONE ZTNA são emparelhados com o Forcepoint DLP, as organizações podem implementar políticas de segurança de dados em todos os lugares em que ele reside – a nuvem, a web e em aplicativos web privados. Isso permite uma estratégia de segurança de dados uniforme e o gerenciamento de políticas consolidadas.
Com tudo isso em mente, o SASE melhora a segurança de dados em um ambiente de nuvem, simplificando sua implementação e manutenção. As organizações obtêm todos os benefícios do SASE, como o gerenciamento simplificado e as economias de despesas, bem como a confiabilidade de uma postura de segurança de dados robusta.













