Seguridad de Datos Nativa de AI
Seguridad de Datos Autogestionada
Ve cuando los datos llegan a IA. Adáptate al riesgo rápidamente. Protege a escala.
Encontrar y etiquetar cualquier dato confidencial
Descripción: Obtenga visibilidad y control sobre los datos estructurados y no estructurados.
Prevén filtraciones. En todas partes.
Proteja los datos confidenciales en IA, la nube, la web, el correo electrónico y los endpoints.
Controla el acceso. Minimiza el riesgo.
Aplica el mínimo privilegio. Encontra archivos con permisos excesivos. Acceso de auditoría.
Más de 12.000 clientes no podían equivocarse










































Los riesgos de datos son complejos.
Forcepoint Data Security Cloud lo simplifica.
Clasifique con contexto
AI Mesh proporciona claridad confiable sobre la confidencialidad de sus datos.
Unifique la gestión de políticas
Combine las capacidades de DSPM, DLP, DDR, CASB y SWG en una plataforma.
Aplique en cualquier lugar
Aplique políticas en la nube, la web, el endpoint, el correo electrónico y la red en segundos.
Sepa lo que importa
Descubra qué datos tiene y dónde residen.
Adáptese a los riesgos
Ajuste las políticas dinámicamente a medida que surgen las amenazas.
Simplifique la seguridad
Automatice los controles de flujos de trabajo y políticas para todos los canales.

Protege tus datos.
Protege tu negocio.
Explora nuestras soluciones para:
Detenga la pérdida de datos y simplifique el cumplimiento
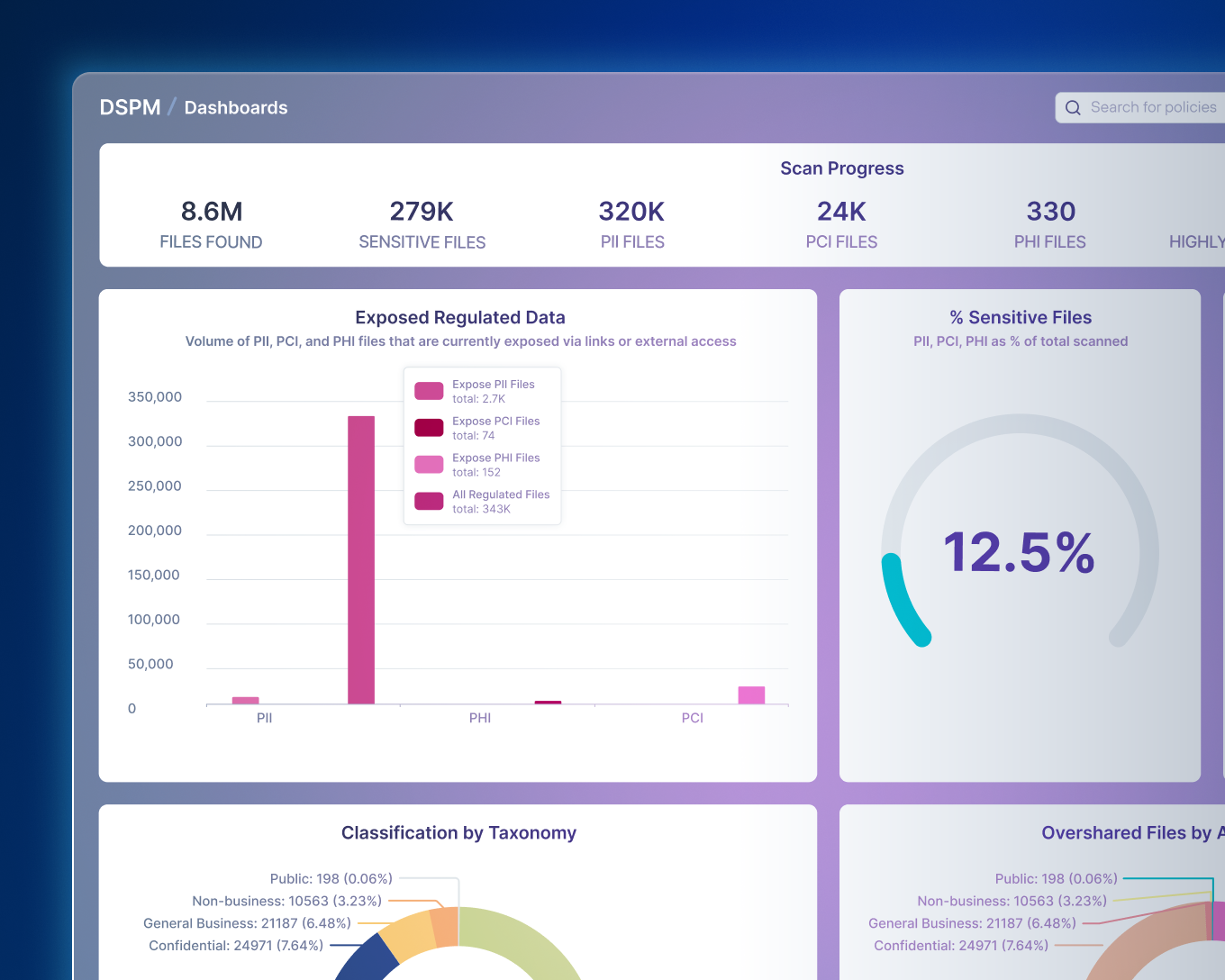
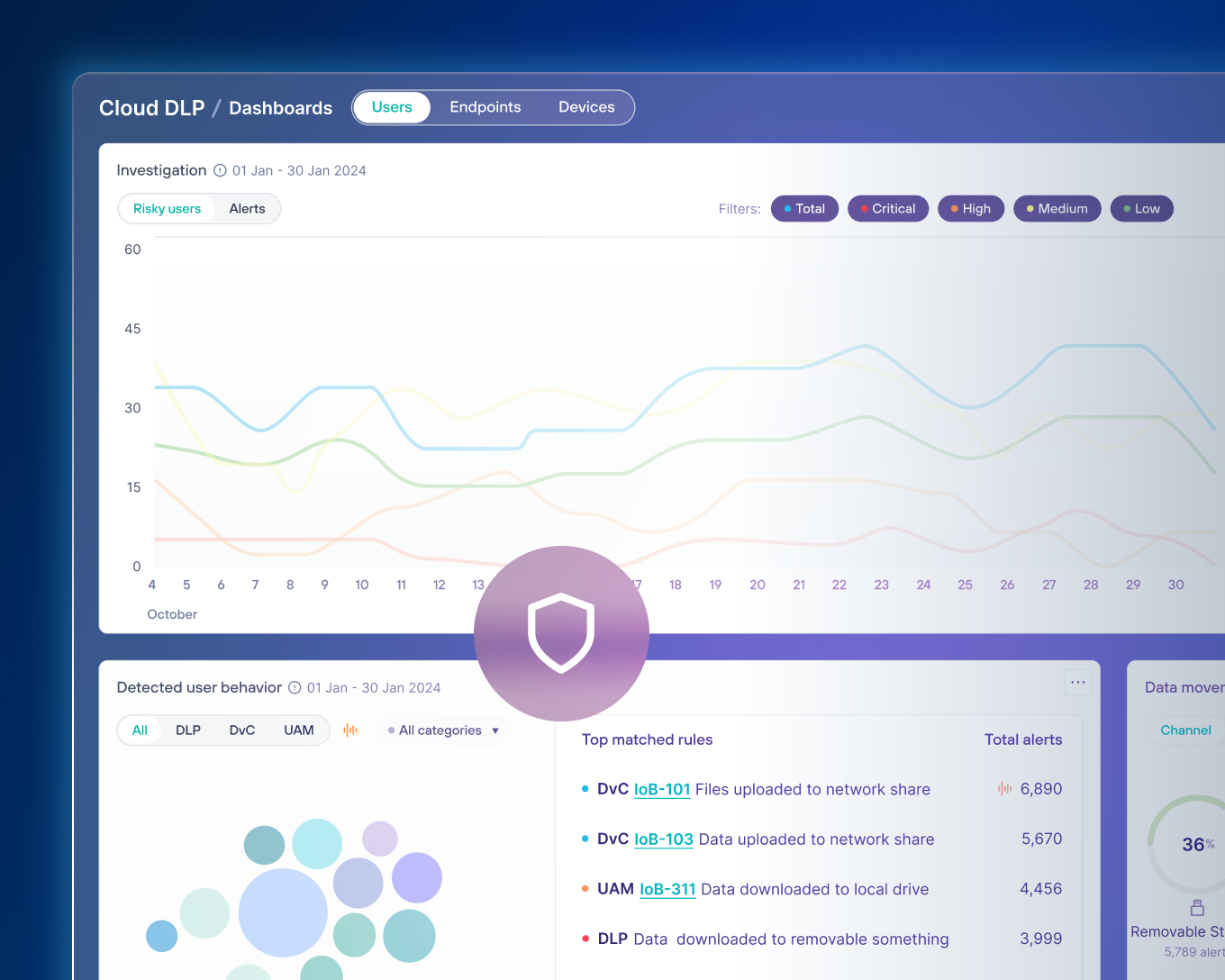
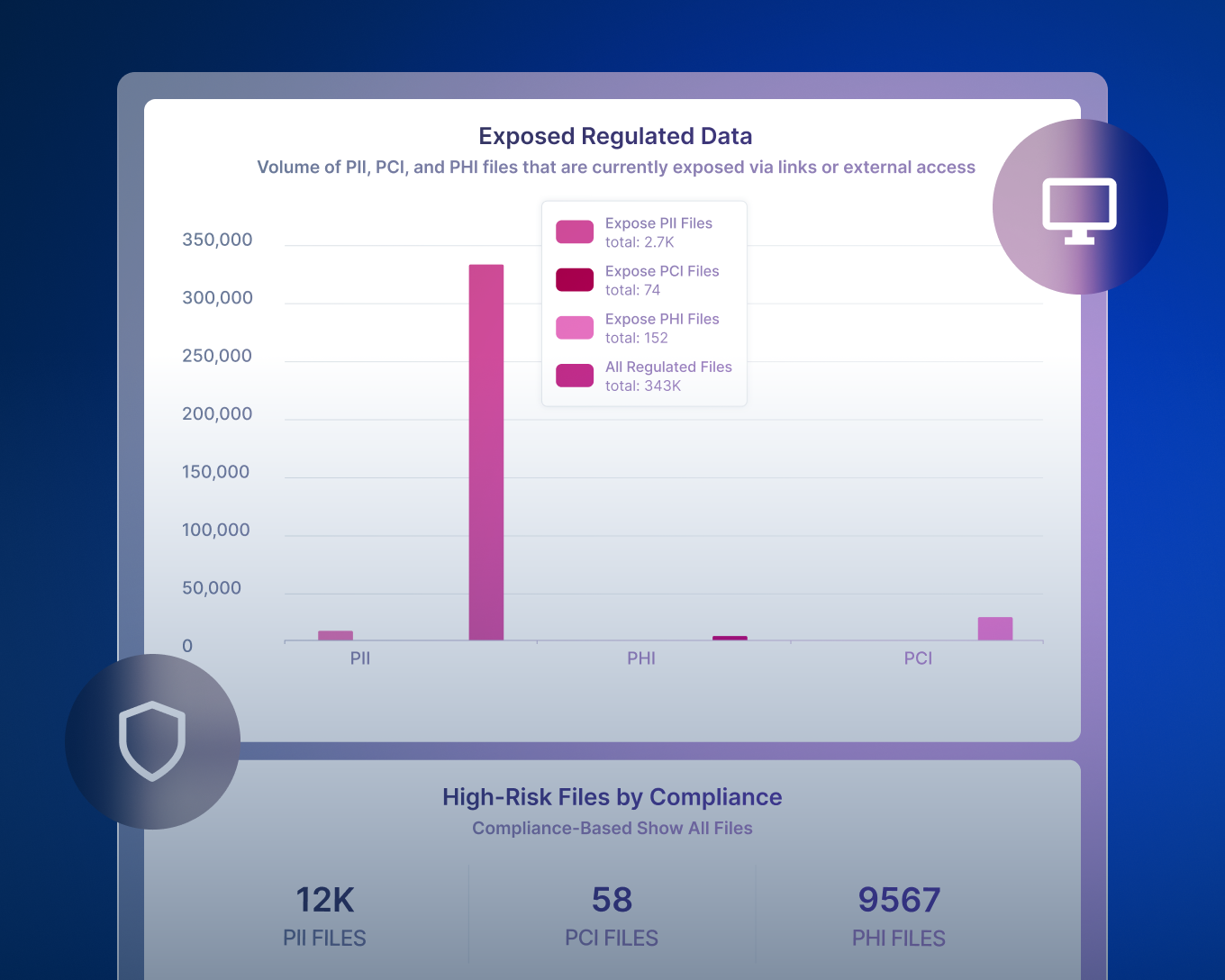



Presentación: Detección y Respuesta de Datos
Forcepoint Data Detection and Response (DDR) monitorea continuamente los datos para detectar posibles actividades de fuga de datos y evitar las amenazas antes de que ocurran.
Descubra cómo hacerlo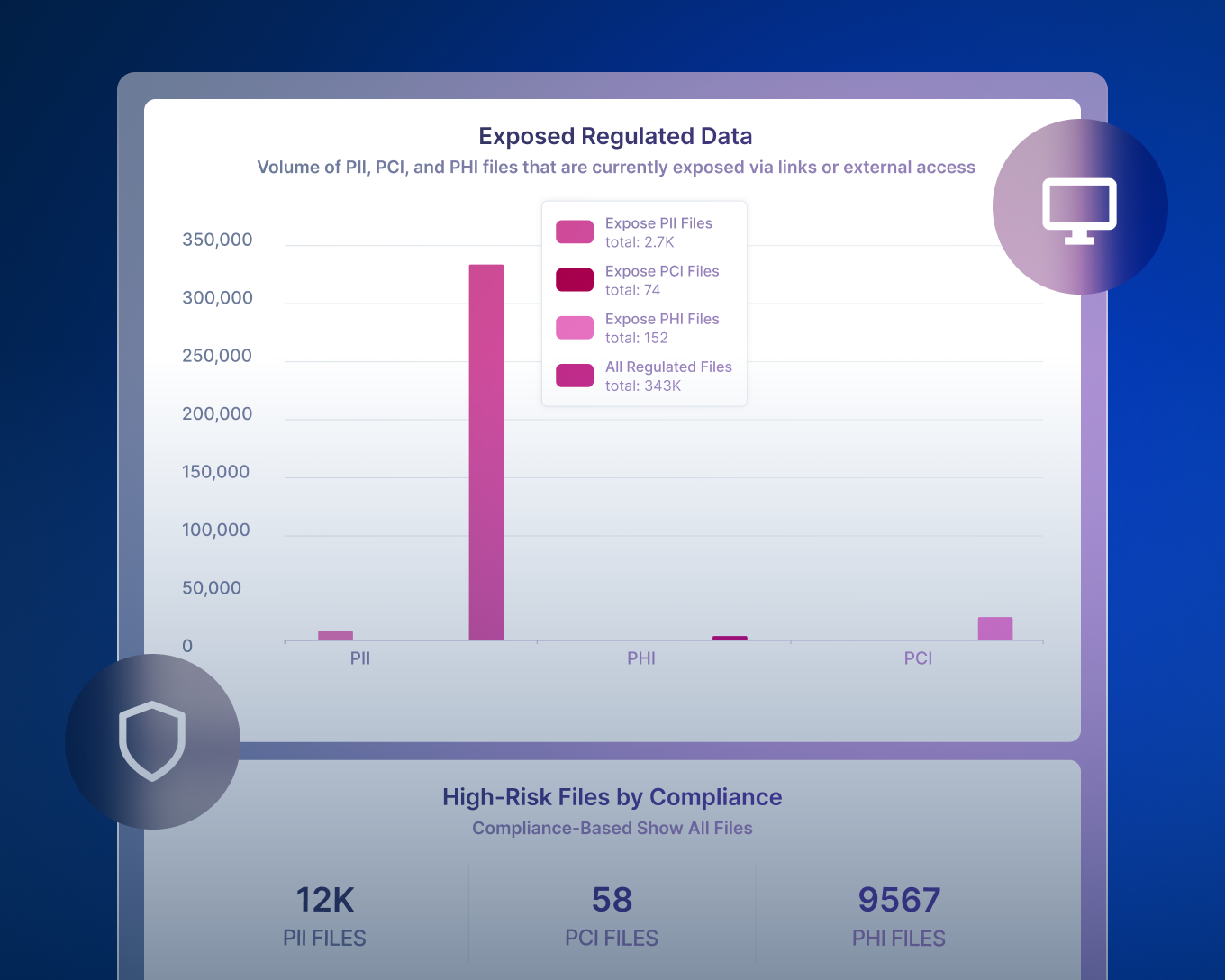
Convierta la Data Security en una ventaja comercial
Todo lo que necesita saber
sobre la Data Security

GUÍA
AI Mesh

GUÍA
Guía ejecutiva para DSPM

EBOOK
Guía del comprador de DLP

GUÍA
La guía práctica para ejecutivos sobre Data Security
Comenzar tu Data Risk Assessment
