KI-native Datensicherheit
Intelligente Datensicherheit
Erkennen Sie, wenn Daten auf KI treffen, passen Sie sich schnell an Risiken an und gewährleiten Sie Sicherheit im großen Stil.
Alle sensiblen Daten finden und markieren
Verschaffen Sie sich Transparenz und Kontrolle über strukturierte und unstrukturierte Daten.
Verhindern Sie Sicherheitsverletzungen überall.
Schützen Sie sensible Daten über KI, Cloud, Web, E-Mail und Endpoints hinweg.
Zugriff kontrollieren und Risiken minimieren
Setzen Sie das Least-Privilege-Prinzip durch, finden Sie Dateien mit übermäßigen Berechtigungen und prüfen Sie Zugriffe.
Über 12.000 Kunden können sich nicht irren










































Datenrisiken sind komplex.
Forcepoint Data Security Cloud vereinfacht sie.
Mit Kontext klassifizieren
AI Mesh bietet zuverlässige Klarheit über die Sensibilität Ihrer Daten.
Richtlinienverwaltung vereinheitlichen
Kombinieren Sie die Funktionen von DSPM, DLP, DDR, CASB und SWG auf einer Plattform.
Überall durchsetzen
Wenden Sie Richtlinien in der Cloud, im Internet, beim Endbenutzer, in E-Mail und im Netzwerk in Sekunden an.
Wissen, was zählt
Erfahren Sie, welche Daten Sie haben und wo sie sich befinden.
An Risiken anpassen
Passen Sie Richtlinien dynamisch an, wenn neue Bedrohungen auftauchen.
Vereinfachen Sie die Sicherheit
Automatisieren Sie Workflow- und Richtlinienkontrollen für alle Kanäle.

Protect Your Data.
Protect Your Business.
Explore our solutions for:
Datenverlust verhindern und die Compliance vereinfachen
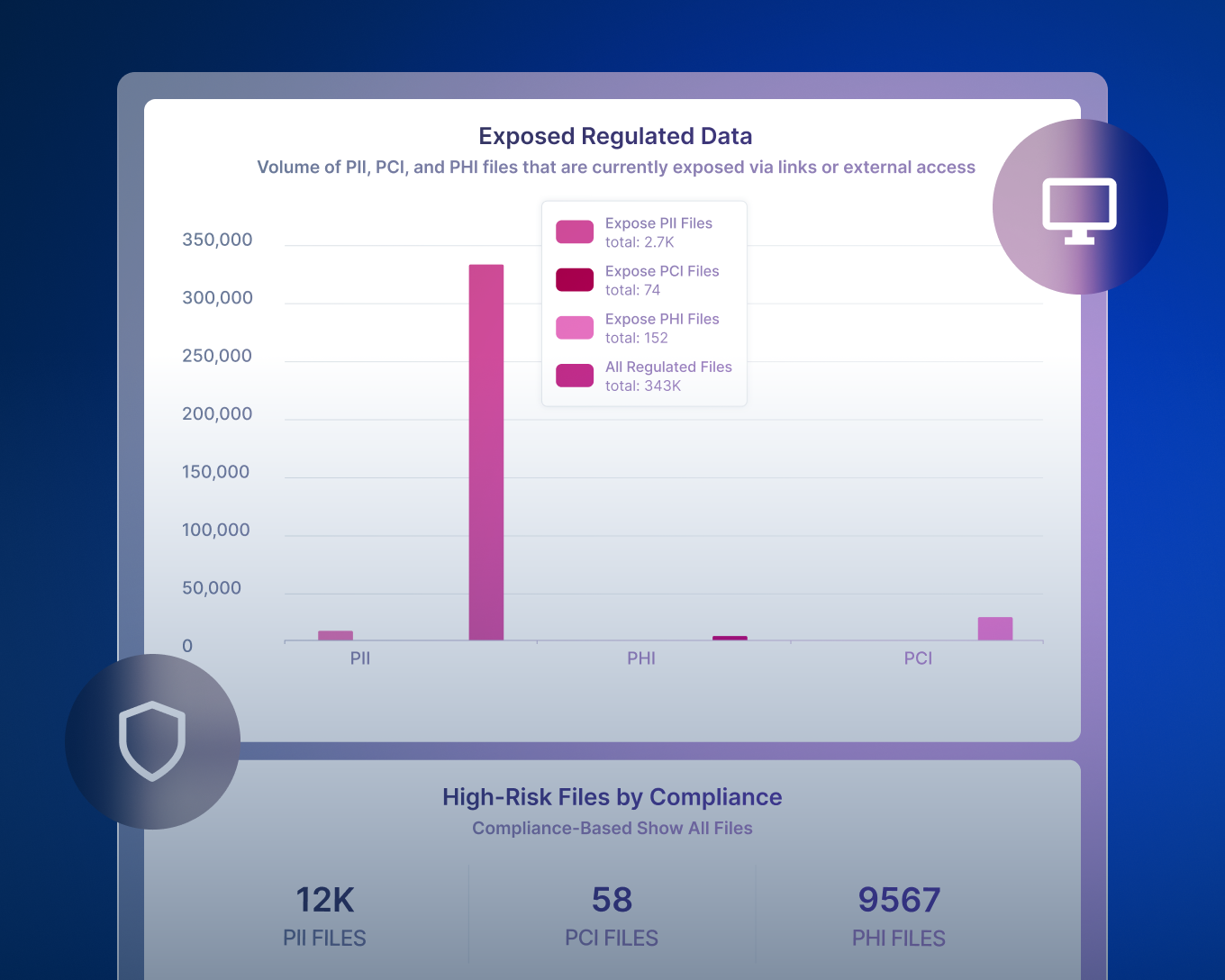



Wir präsentieren: Data Detection and Response (DDR)
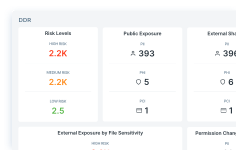
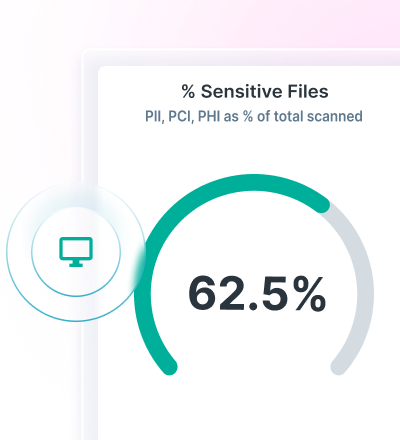
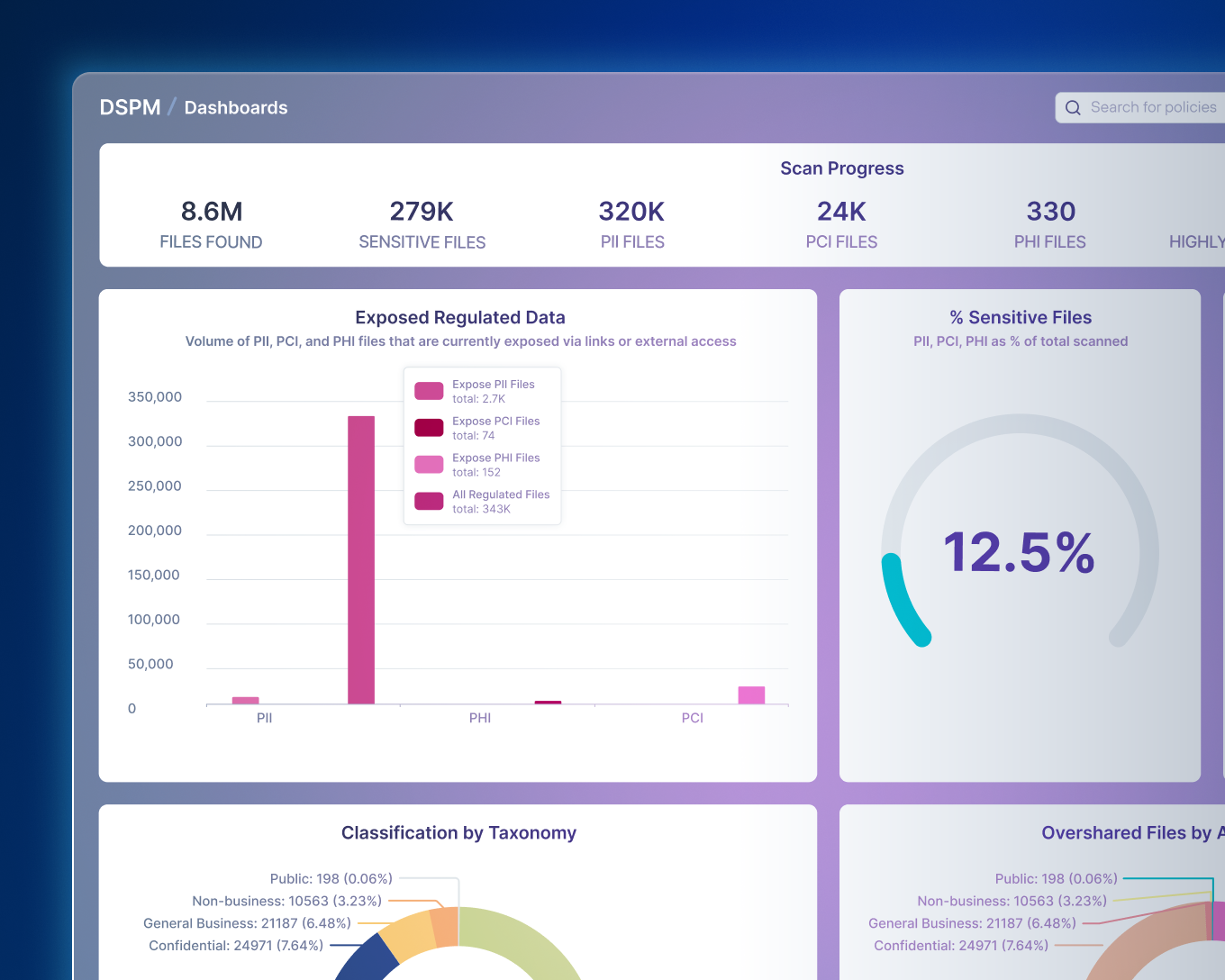
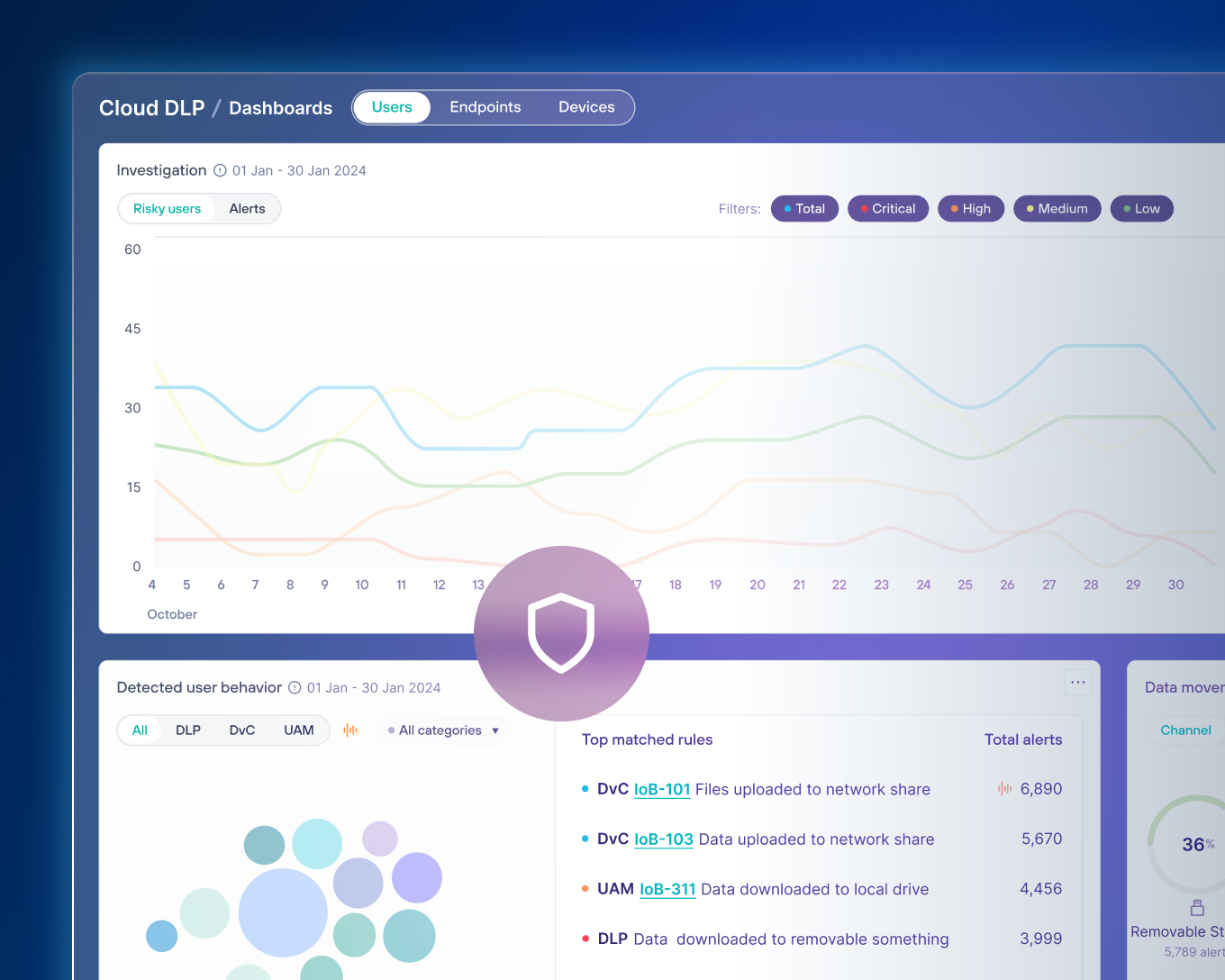
Forcepoint Data Detection and Response (DDR) überwacht Daten kontinuierlich, um potenzielle Datenverletzungsaktivitäten zu erkennen und Bedrohungen zu verhindern, bevor sie auftreten.
So funktioniert es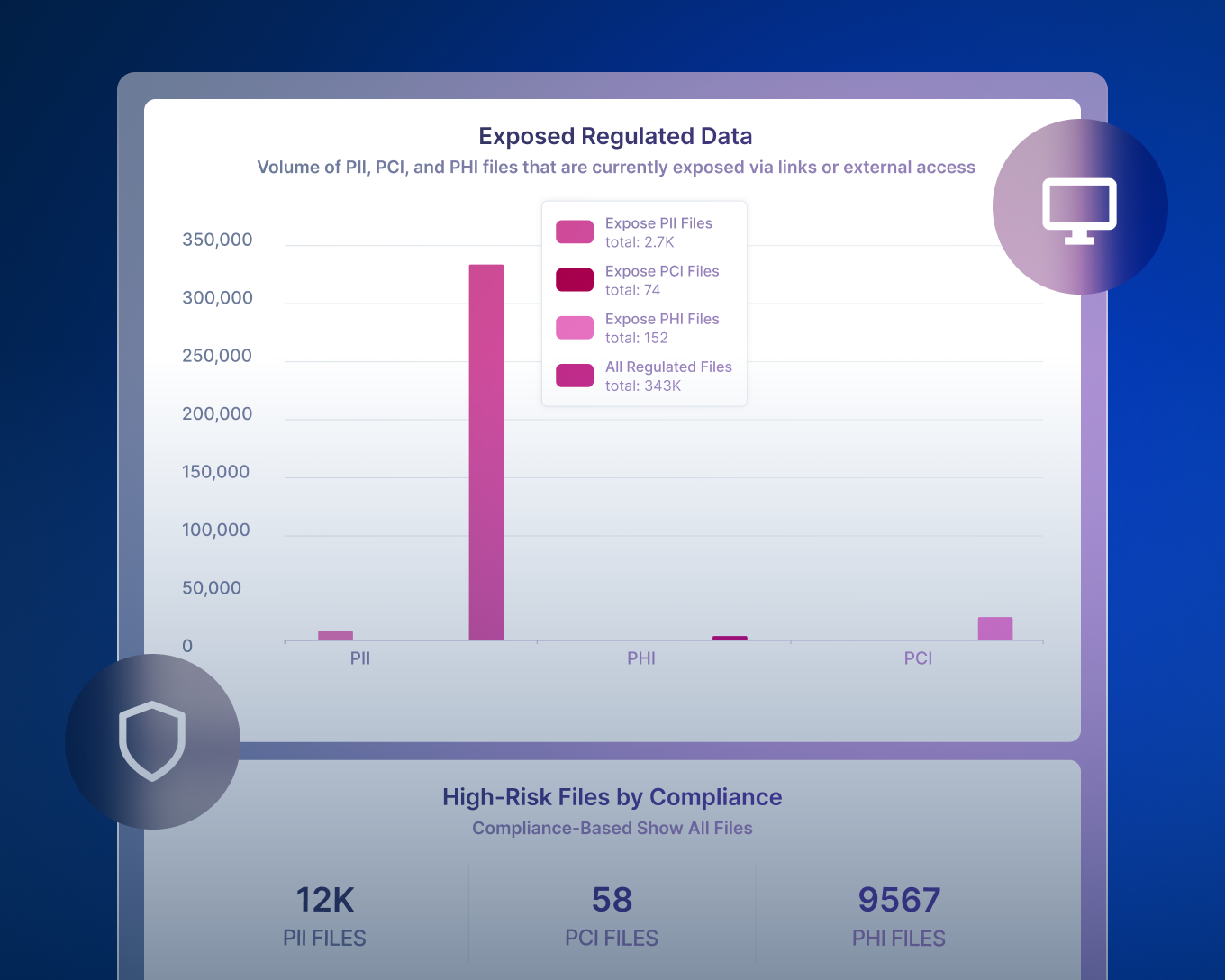
Verwandeln Sie Datensicherheit in einen Geschäftsvorteil
Alles, was Sie über Datensicherheit
wissen müssen

LEITFADEN
AI Mesh

LEITFADEN
Leitfaden für DSPM

EBOOK
Der Leitfaden beim Kauf von DLP-Lösungen

LEITFADEN
Der praktische Leitfaden für Führungskräfte zur Datensicherheit
Start Your Data Risk Assessment